In an age where wellness trends come and go, understanding blood sugar and insulin has emerged as a cornerstone of lasting health. Did you know that mastering these concepts can lead to improved energy levels, weight management, and even mood stability? In “Unlock the Secrets of Blood Sugar and Insulin for Better Health!”, we delve into the crucial relationship between these two elements and how they impact your overall well-being. Join us as we explore actionable insights that could transform your health journey and empower you to take control of your body like never before!
What is Blood Sugar?
Definition and Importance
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream. It serves as the primary source of energy for your body’s cells. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is essential for optimal bodily functions. When blood sugar levels fluctuate—whether spiking or dropping—this can lead to various health issues, including diabetes.
| Blood Sugar Level | Description | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 70 mg/dL | Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) | Eat fast-acting carbs |
| 70-99 mg/dL | Normal fasting level | No action needed |
| 100-125 mg/dL | Prediabetes | Lifestyle changes needed |
| 126 mg/dL or higher | Diabetes diagnosed | Consult healthcare provider |
- Key Takeaways:
- Blood sugar is essential for energy.
- Fluctuations can cause serious health issues.
- Monitoring is crucial for overall health.
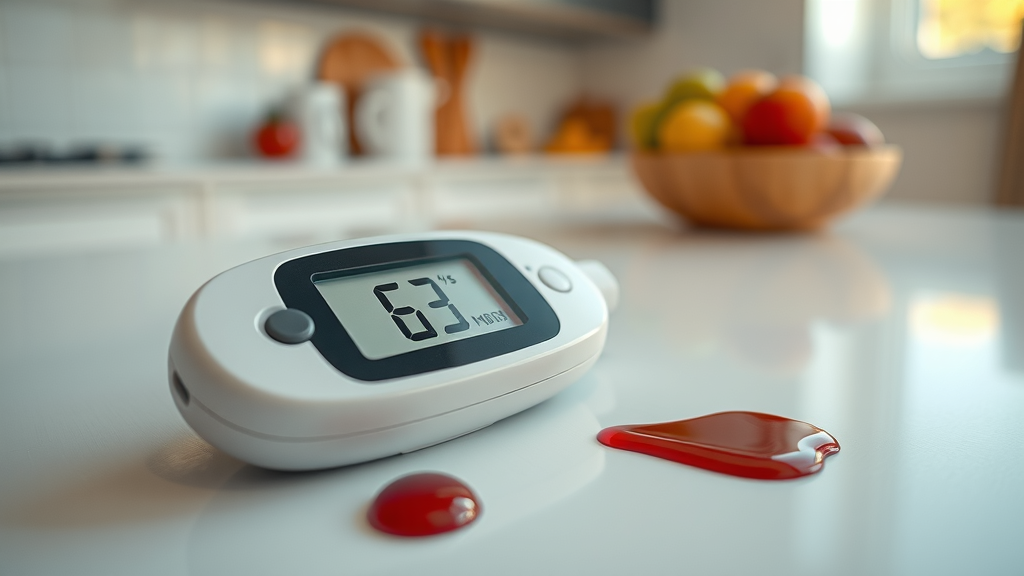

How Blood Sugar Levels are Measured
Blood sugar levels are typically measured using a blood glucose monitor. This device requires a small drop of blood, usually obtained by pricking the side of your fingertip with a lancet. The reading is shown in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
-
Common Measurement Methods:
1. Fasting Blood Glucose Test: Measures levels after not eating for at least 8 hours.
2. Postprandial Test: Taken 2 hours after eating to gauge how well the body manages glucose.
3. A1C Test: Provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past three months.
“Understanding how to measure and interpret your blood sugar levels can empower you to make informed choices about your health.”
The Role of Insulin in Blood Sugar Regulation
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels. It allows cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
| Insulin Function | Description | Impact on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose uptake | Moves glucose into cells | Lowers blood sugar |
| Storage | Converts glucose to glycogen | Reduces blood sugar |
| Fat storage | Converts excess glucose to fat | Increases fat reserves |
- Key Functions of Insulin:
- Facilitates energy utilization by delivering glucose to cells.
- Promotes storage of excess glucose for later use.
- Regulates blood sugar levels to maintain homeostasis.
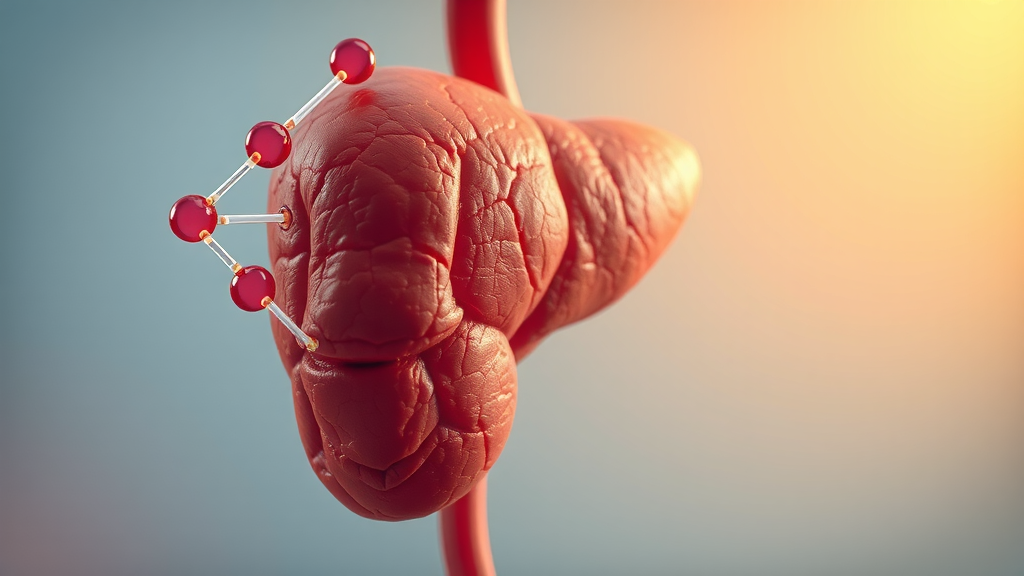
How Insulin Works
Insulin acts like a key that unlocks cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy. This process is vital for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
-
Step-by-Step Process:
1. When you eat, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose.
2. The pancreas releases insulin in response to increased blood sugar levels.
3. Insulin facilitates the entry of glucose into cells.
4. Blood sugar levels decrease as glucose is utilized or stored.
“Insulin is essential for energy management and overall metabolic health.”
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Normal and Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels can be categorized into normal, prediabetic, and diabetic ranges. Knowing these levels is essential for effective management and prevention strategies.
- Normal Ranges:
- Fasting: 70-99 mg/dL
-
Postprandial: Less than 140 mg/dL
-
Abnormal Levels:
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): Levels above 126 mg/dL can lead to serious complications.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): Levels below 70 mg/dL can cause symptoms like dizziness and confusion.
High Blood Sugar Levels (Hyperglycemia)
Hyperglycemia is a condition where excess glucose accumulates in the bloodstream. This can be caused by:
- Insufficient insulin production.
- Poor dietary choices high in carbohydrates.
- Lack of physical activity.
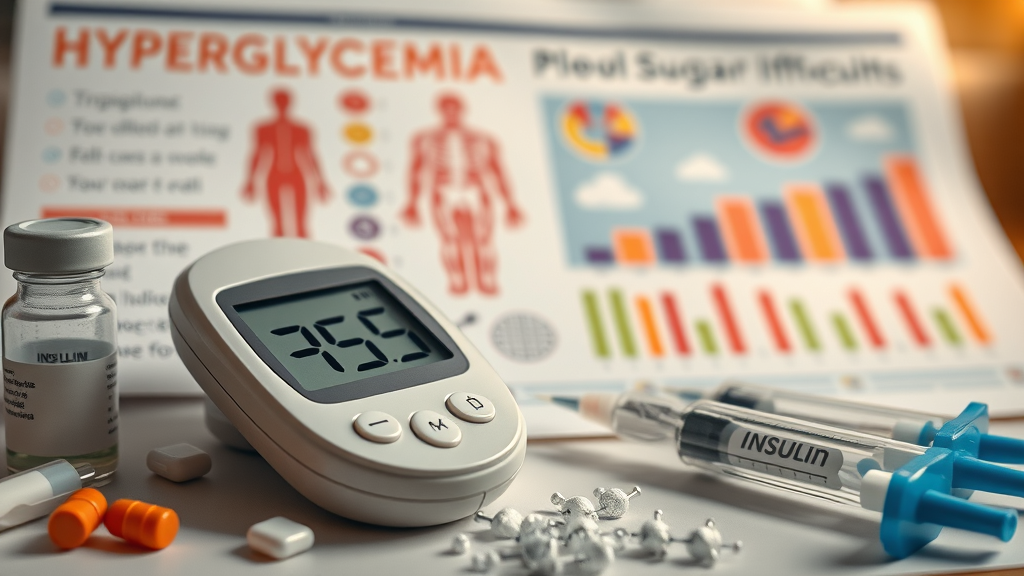
Low Blood Sugar Levels (Hypoglycemia)
Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low. Symptoms may include:
- Sweating and shaking.
- Dizziness and confusion.
- Fatigue and weakness.

Diet and Lifestyle Impact on Blood Sugar
The Importance of Meal Planning
A well-structured meal plan is vital for managing blood sugar levels. It helps ensure that you consume balanced meals that stabilize glucose levels.
-
Meal Planning Tips:
1. Include a variety of food groups.
2. Monitor portion sizes.
3. Focus on complex carbohydrates.
4. Stay hydrated.
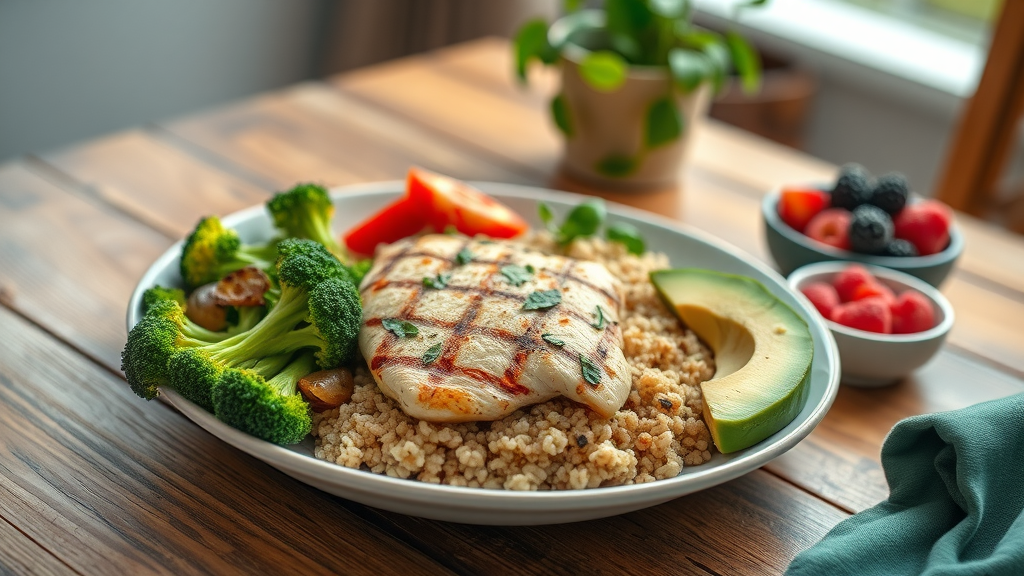

Foods to Include and Avoid
Certain foods can help manage blood sugar levels effectively:
- Foods to Include:
- Whole grains.
- Lean proteins.
-
Healthy fats (e.g., avocados, nuts).
-
Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary snacks and beverages.
- Highly processed foods.
- Refined carbohydrates.
Physical Activity and Blood Sugar Management
Regular physical activity can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels.
- Recommended Activities:
- Aerobic exercises (walking, running).
- Strength training.
- Flexibility exercises (yoga, stretching).

Managing Diabetes and Blood Sugar Levels
Types of Diabetes
Understanding the different types of diabetes is crucial for effective management:
| Type of Diabetes | Description |
|---|---|
| Type 1 | Autoimmune condition; insulin-dependent |
| Type 2 | Insulin resistance; often preventable |
| Gestational | Occurs during pregnancy; usually temporary |
- Management Strategies:
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar.
- Medication adherence.
- Lifestyle modifications.

Medical Care and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with your healthcare team are vital for managing diabetes effectively. They can provide personalized guidance on:
- Medication management.
- Blood sugar monitoring.
- Dietary recommendations.
Key Takeaways on Blood Sugar and Insulin
Essential Insights
- Understanding blood sugar and insulin is crucial for overall health.
- Regular monitoring can prevent complications related to diabetes.
- A balanced diet and active lifestyle are essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Resources for Further Learning
For those interested in diving deeper into blood sugar management, consider visiting the American Diabetes Association for comprehensive resources.

Video Resource
For a visual explanation of blood sugar management, check out this informative video: Understanding Blood Sugar and Insulin.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is a normal blood sugar level?
- A normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70-99 mg/dL. -
How can I manage high blood sugar?
- Regular monitoring, medication, and lifestyle changes are key. -
What foods can help lower blood sugar?
- Foods high in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats are beneficial.
Conclusion
Understanding blood sugar and insulin is essential for maintaining good health and managing diabetes effectively. By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can take control of their health and minimize the risk of complications.
- Key Takeaways:
- Blood sugar levels should be monitored regularly.
- Insulin plays a crucial role in glucose regulation.
- A healthy lifestyle can significantly improve blood sugar control.
With this knowledge, you are now better equipped to manage your health and make informed choices about your well-being.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 





Write A Comment